11 月 . 04, 2024 11:11 Back to list
Wafer Butterfly Valve Manufacturing Process and Quality Control Techniques
The Wafer Butterfly Valve An Essential Component in Modern Engineering
In the realm of fluid control, the wafer butterfly valve stands out as a pivotal innovation that seamlessly combines functionality with efficiency. Unlike traditional valves, the wafer butterfly valve is designed without flanges, making it a compact, lightweight option ideal for a variety of industrial applications. This article explores the manufacturing processes, advantages, and applications of wafer butterfly valves, spotlighting their significance in modern engineering.
Understanding Wafer Butterfly Valves
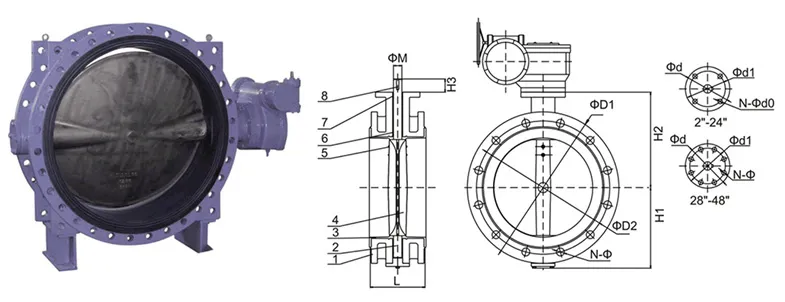
At its core, a wafer butterfly valve consists of a circular disc with a central shaft. When the valve is closed, the disc obstructs the flow of liquid or gas. Conversely, when it is opened, the disc rotates perpendicular to the flow, allowing for unobstructed passage. The simplicity of the design lends itself to straightforward operation, which can be manual or automated, depending on the specific requirements of an installation.
Manufacturing Process
The fabrication of wafer butterfly valves involves several key steps, ensuring durability and performance. First, high-quality materials such as stainless steel, cast iron, and polymer composites are selected based on the intended application. These materials are chosen for their resistance to corrosion, pressure, and temperature variations.
The manufacturing process typically begins with casting or machining the valve body. Precision machining ensures that the valve meets stringent dimensional tolerances, critical for proper sealing and operation. The disc and shaft are also manufactured with high precision, often requiring a series of tests for strength and flexibility.
Once the components are ready, they undergo assembly, where seals and gaskets are installed to prevent leakage. Advanced techniques such as robotic welding may be employed to enhance the reliability of the joints. Quality control checks at various stages of production are crucial, as they ensure that the valves meet industry standards and are free from defects.
Advantages of Wafer Butterfly Valves
wafer butterfly valve factory
The wafer butterfly valve offers numerous advantages over traditional valve types. One of the primary benefits is its space-saving design, which allows for installation in tight spaces where other valves may not fit. This compactness also results in lighter weight, simplifying transportation and installation.
Additionally, wafer butterfly valves exhibit low operational torque, meaning they require less energy to open and close, contributing to energy savings in systems they are installed in. Their design also facilitates a quick and straightforward installation process, often involving just bolting the valve between two flanges in a pipeline.
Moreover, these valves provide excellent control over flow rates, making them ideal for modulating services. Their ability to handle a wide range of pressures and temperatures also makes them suitable for diverse applications, from water treatment plants to chemical processing facilities.
Applications
The versatility of wafer butterfly valves means they find applications across various sectors. In water management systems, they are used to regulate flow in pipelines and storage tanks. In the chemical industry, they control fluid flow in reactors and other equipment, where precise regulation is crucial.
Moreover, wafer butterfly valves are increasingly being employed in the HVAC industry for airflow control in heating and cooling systems. The food and beverage industry also benefits from their use, where hygiene standards are paramount, and compact designs are advantageous.
Conclusion
As industries continue to evolve, the demand for efficient, reliable fluid control solutions will only grow. The wafer butterfly valve, with its innovative design, effective performance, and broad range of applications, represents an essential component in the toolbox of modern engineering. Its manufacturing advances ensure that it will remain a vital part of infrastructure development and maintenance in the years to come, reinforcing its place in ensuring the integrity and efficiency of fluid systems worldwide.
Share
-
Understanding the Differences Between Wafer Type Butterfly Valve and Lugged Butterfly ValveNewsOct.25,2024
-
The Efficiency of Wafer Type Butterfly Valve and Lugged Butterfly ValveNewsOct.25,2024
-
The Ultimate Guide to Industrial Swing Check Valve: Performance, Installation, and MaintenanceNewsOct.25,2024
-
Superior Performance with Industrial Swing Check Valve: The Essential Valve for Any SystemNewsOct.25,2024
-
Industrial Swing Check Valve: The Ideal Solution for Flow ControlNewsOct.25,2024
-
You Need to Know About Industrial Swing Check Valve: Functionality, Scope, and PerformanceNewsOct.25,2024