10 月 . 06, 2024 15:18 Back to list
underground cable wire
Understanding Underground Cable Wires A Key Component of Modern Infrastructure
In the age of rapid technological advancement, the need for reliable and efficient electrical transmission systems cannot be overstated. One of the most critical components in this infrastructure is underground cable wires. These cables, concealed beneath the earth's surface, play an essential role in delivering electricity and telecommunications services while minimizing the impact on the environment and urban landscape.
What are Underground Cable Wires?
Underground cable wires are insulated electrical cables designed to operate below the ground. Unlike overhead power lines, which are exposed to the elements and can be susceptible to environmental factors such as wind, ice, and lightning, underground cables are safeguarded by their subterranean placement. This design not only ensures a continuous supply of power but also reduces the visual and aesthetic impact on communities.
There are various types of underground cables, including those used for power transmission, telecommunications, and data transfer. Power cables typically consist of multiple conductive materials such as copper or aluminum, insulated to prevent electrical leakage and damage. Telecommunications cables often employ similar structures but may include fiber optic components to facilitate high-speed internet and data services.
Benefits of Underground Cables
1. Enhanced Reliability One of the primary advantages of underground cables is their increased reliability. By being insulated from harsh weather conditions and physical damage from falling branches or vehicles, these cables are less likely to experience outages, leading to a more stable electrical supply.
2. Safety With power cables buried underground, the risks associated with electrical shocks and accidents are significantly reduced. This is particularly important in residential areas, where children and pets may be present. Furthermore, underground installations are less likely to be affected by natural disasters, providing an additional layer of safety for communities.
underground cable wire
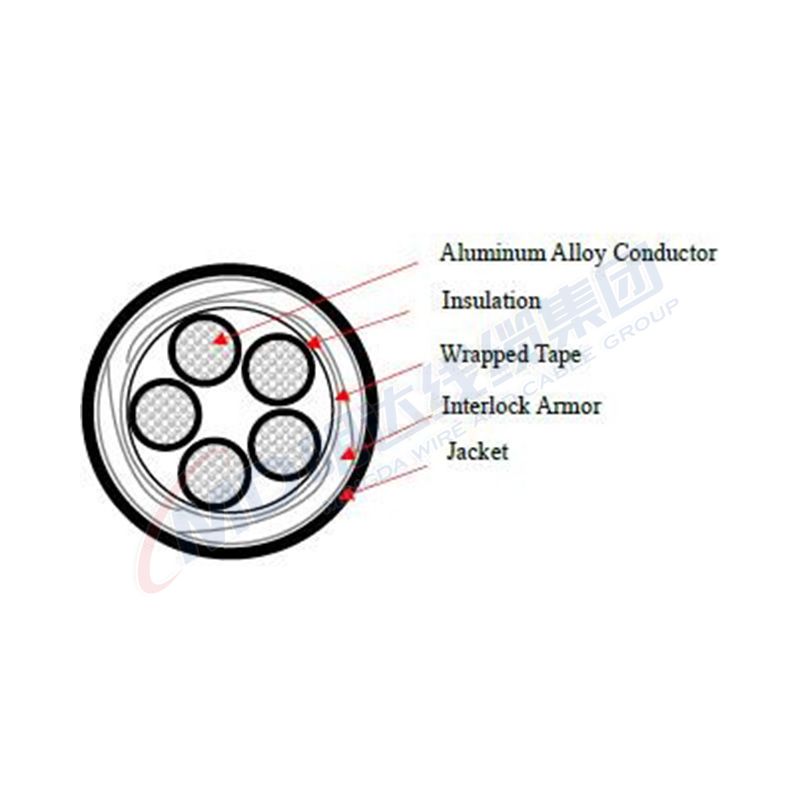
3. Aesthetic Appeal Underground cabling eliminates the eyesores of overhead wires and pole structures, allowing for more visually appealing urban landscapes. This is particularly valuable in historic districts or densely populated areas where maintaining a specific aesthetic is crucial.
4. Reduced Maintenance While underground cables can be more expensive to install initially, they often require less maintenance over time. The risks of damage from environmental factors are significantly minimized, leading to lower long-term costs for utility companies and municipalities.
Challenges of Installation and Maintenance
Despite the numerous advantages of underground cable systems, there are several challenges associated with their installation and maintenance. The cost of laying these cables is typically higher than that of overhead lines due to the need for excavation and specialized machinery. Additionally, locating and repairing underground cables can be complex, requiring skilled personnel and advanced technology such as ground-penetrating radar.
Moreover, urban environments present logistical challenges, as utilities must navigate existing underground systems, including water, gas, and sewage lines. Effective coordination and planning are crucial to ensure that the installation does not disrupt other services or damage existing infrastructure.
Conclusion
As communities continue to evolve and expand, the demand for reliable power and communication systems will only grow. Underground cable wires offer a sustainable solution to meet these needs, providing a reliable, safe, and aesthetically pleasing alternative to traditional overhead lines. By investing in underground infrastructure, cities can ensure a resilient energy future while enhancing the quality of life for their residents. As technology progresses and challenges are addressed, we can expect to see underground cables becoming an integral part of our modern landscape.
Share
-
Understanding the Differences Between Wafer Type Butterfly Valve and Lugged Butterfly ValveNewsOct.25,2024
-
The Efficiency of Wafer Type Butterfly Valve and Lugged Butterfly ValveNewsOct.25,2024
-
The Ultimate Guide to Industrial Swing Check Valve: Performance, Installation, and MaintenanceNewsOct.25,2024
-
Superior Performance with Industrial Swing Check Valve: The Essential Valve for Any SystemNewsOct.25,2024
-
Industrial Swing Check Valve: The Ideal Solution for Flow ControlNewsOct.25,2024
-
You Need to Know About Industrial Swing Check Valve: Functionality, Scope, and PerformanceNewsOct.25,2024