2 月 . 18, 2025 10:16 Back to list
Resilient Seat Gate Valve
The 2-inch ball check valve is a vital component in diverse industrial settings, offering unmatched reliability and efficiency. This crucial piece of equipment is engineered to allow fluids to flow in one direction, thereby preventing backflow and ensuring system integrity. Understanding its operational prowess, construction intricacies, and strategic applications is essential for professionals seeking to optimize fluid-handling systems.
Furthermore, the installation of the 2-inch ball check valve is crucial to its operation. It must be aligned correctly to ensure the gravitational forces or internal pressures accurately guide the ball into the seated position during reverse flow attempts. Regular maintenance checks, although minimal with these valves, can further ensure continued performance. Periodic cleaning and inspection for wear or corrosion can mitigate the risk of failures and prolong the service life of the valve. Authoritative professionals in the field acknowledge that the choice of a 2-inch ball check valve can significantly influence not only the efficiency of a given system but also its overall operational costs. By preventing backflow effectively, these valves protect pumps and other devices from potential damage, thereby lowering repair costs and reducing downtime. In large-scale industrial operations, the economic impact of reduced wear on expensive machinery cannot be overstated. Trust in the 2-inch ball check valve derives from its proven history and reliability across industries. From water treatment plants to chemical manufacturing, its application breadth is vast. Engineers and system designers continually turn to these valves for their predictable, low-maintenance operation that ensures safety and efficiency. It is not merely a component but an assurance of regulatory compliance, operational smoothness, and environmental responsibility. In conclusion, the 2-inch ball check valve stands out as a paragon of fluid control engineering. Its deceptively simple design masks a complexity of function that is indispensable to the modern industrial tapestry. By selecting and utilizing these valves with a well-informed understanding of their properties and potential applications, industry professionals can unlock unparalleled system efficiency and reliability. Investing in the right valve not only safeguards operations but also underpins the foundational trust in industries that rely on precise fluid management.
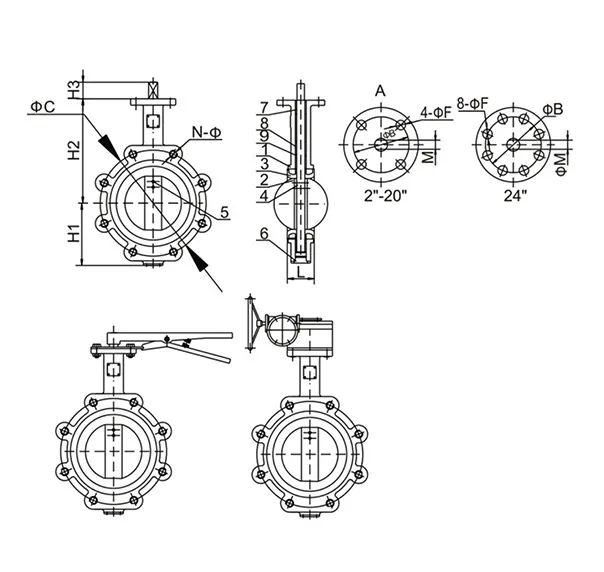

Furthermore, the installation of the 2-inch ball check valve is crucial to its operation. It must be aligned correctly to ensure the gravitational forces or internal pressures accurately guide the ball into the seated position during reverse flow attempts. Regular maintenance checks, although minimal with these valves, can further ensure continued performance. Periodic cleaning and inspection for wear or corrosion can mitigate the risk of failures and prolong the service life of the valve. Authoritative professionals in the field acknowledge that the choice of a 2-inch ball check valve can significantly influence not only the efficiency of a given system but also its overall operational costs. By preventing backflow effectively, these valves protect pumps and other devices from potential damage, thereby lowering repair costs and reducing downtime. In large-scale industrial operations, the economic impact of reduced wear on expensive machinery cannot be overstated. Trust in the 2-inch ball check valve derives from its proven history and reliability across industries. From water treatment plants to chemical manufacturing, its application breadth is vast. Engineers and system designers continually turn to these valves for their predictable, low-maintenance operation that ensures safety and efficiency. It is not merely a component but an assurance of regulatory compliance, operational smoothness, and environmental responsibility. In conclusion, the 2-inch ball check valve stands out as a paragon of fluid control engineering. Its deceptively simple design masks a complexity of function that is indispensable to the modern industrial tapestry. By selecting and utilizing these valves with a well-informed understanding of their properties and potential applications, industry professionals can unlock unparalleled system efficiency and reliability. Investing in the right valve not only safeguards operations but also underpins the foundational trust in industries that rely on precise fluid management.
Share
Next:
Latest news
-
Understanding the Differences Between Wafer Type Butterfly Valve and Lugged Butterfly ValveNewsOct.25,2024
-
The Efficiency of Wafer Type Butterfly Valve and Lugged Butterfly ValveNewsOct.25,2024
-
The Ultimate Guide to Industrial Swing Check Valve: Performance, Installation, and MaintenanceNewsOct.25,2024
-
Superior Performance with Industrial Swing Check Valve: The Essential Valve for Any SystemNewsOct.25,2024
-
Industrial Swing Check Valve: The Ideal Solution for Flow ControlNewsOct.25,2024
-
You Need to Know About Industrial Swing Check Valve: Functionality, Scope, and PerformanceNewsOct.25,2024